A formal expression of opinion or intention made, usually after voting, by a formal organization, a legislature, a club, or other group.Compare concurrent resolution, joint resolution. A resolve; a decision or determination: to make a firm resolution to do something. A 'Plot' Resolution A tit for tat response. Within the framework of the follow-up of the 14 March 2016 decision adopted pursuant to Article. The Shadow of ICC. ICC has opened a preliminary examination into crimes committed in Burundi. The resolution initiated. 'Let me make fun of the EU'.
What Is A Plot Diagram?
A plot diagram is a graphical representation of the plot of the story. A story plot diagram is a line graph of story's events, beginning with the story's start on the left and continuing toward the right, ending with the story's conclusion.
[insert drawing of plot diagram based entirely on the one from the existing piece; there's nothing wrong with it]
Whether writing creatively or analyzing another author's writing, you can study the plot structure and storyline using a plot diagram.
- Elements of Plot
Elements Of Plot
The plot of a story is the unfolding sequence of events. Just about every story has the same parts of the plot. The six parts of a story are:
- Exposition
- Conflict
- Rising action
- Climax
- Falling action
- Resolution
These six elements break down into three chronological segments. Each segment of the story usually has two elements.
- Beginning – contains the exposition and establishes the story's conflict.
- Middle – contains the rising action and the story's climax.
- Conclusion – contains the falling action and resolution.

Exposition
Exposition in a plot introduces of the story's setting, mood, the main character, supporting characters, and time. Character development happens during this part of the story.
Conflict
Conflict is the problem, crisis, challenge, dilemma, or obstacle presented to the main character.
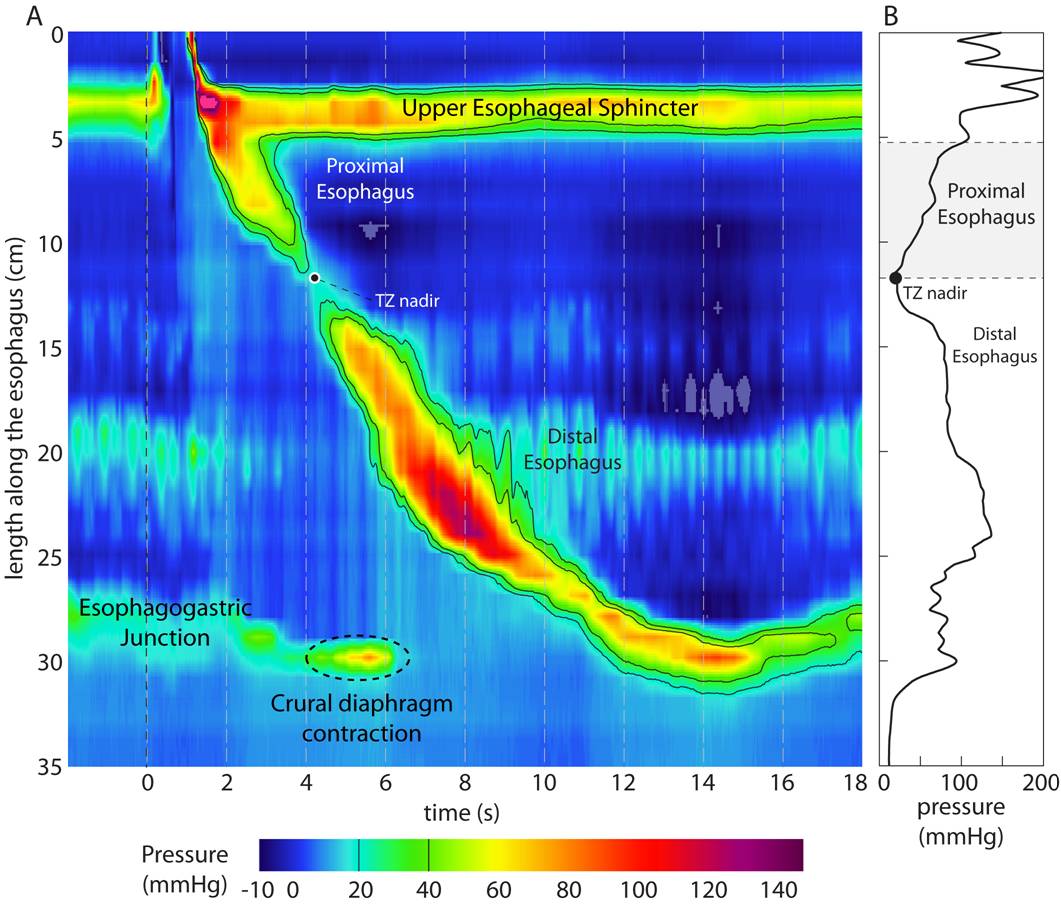
Rising Action
The rising action is a sequence of solutions to the conflict that the main character tries; it is all the events leading to the turning point of the story. It can be identified by increasing tension, emotion, difficulty, or challenge.
Climax
The climax of the story is the peak of excitement, the moment when the story changes (a turning point), the main character, and the problem is resolved.
Falling Action
The Falling action is all the plot points wrapping up, the consequences of the climax, and reflection on the changes in the main character. It can be identified by decreasing tension, an approaching resolution, and relaxation of emotion.
Resolution Of A Story
The resolution is the plot's end, whether that resolution is a happy ending or sad ending, fun or frightening, satisfying or unsatisfying. The resolution might tie up loose ends or leave important elements of the story unresolved.
Plot Diagram Example
We can take the simplest of tales, such as Little Miss Muffet, to practice constructing a plot diagram. Here is the original nursery rhyme:
Little Miss MuffetSat on a tuffet,Eating her curds and whey;Along came a spiderWho sat down beside herAnd frightened Miss Muffet away.
What is the story's beginning? Who is the main character? What is the setting? At the story's beginning, we are introduced to Miss Muffet, who is sitting on a tuffet (a hassock), eating cottage cheese.
In the rising action, what conflict does our main character face? She must deal with the arrival of a spider. The climax of the story is how our main character solves her problem. Miss Muffet's solution to her conflict is to run away. The conclusion of the story is abrupt; Miss Muffet left.
Little Miss Muffet is, admittedly, not a complicated or very interesting story. Yet we can diagram its plot:
With this short story, we see that our graph looks like a triangle. The story plot makes a pyramid shape with an even amount of story on either side of the climax.

Exposition
Exposition in a plot introduces of the story's setting, mood, the main character, supporting characters, and time. Character development happens during this part of the story.
Conflict
Conflict is the problem, crisis, challenge, dilemma, or obstacle presented to the main character.
Rising Action
The rising action is a sequence of solutions to the conflict that the main character tries; it is all the events leading to the turning point of the story. It can be identified by increasing tension, emotion, difficulty, or challenge.
Climax
The climax of the story is the peak of excitement, the moment when the story changes (a turning point), the main character, and the problem is resolved.
Falling Action
The Falling action is all the plot points wrapping up, the consequences of the climax, and reflection on the changes in the main character. It can be identified by decreasing tension, an approaching resolution, and relaxation of emotion.
Resolution Of A Story
The resolution is the plot's end, whether that resolution is a happy ending or sad ending, fun or frightening, satisfying or unsatisfying. The resolution might tie up loose ends or leave important elements of the story unresolved.
Plot Diagram Example
We can take the simplest of tales, such as Little Miss Muffet, to practice constructing a plot diagram. Here is the original nursery rhyme:
Little Miss MuffetSat on a tuffet,Eating her curds and whey;Along came a spiderWho sat down beside herAnd frightened Miss Muffet away.
What is the story's beginning? Who is the main character? What is the setting? At the story's beginning, we are introduced to Miss Muffet, who is sitting on a tuffet (a hassock), eating cottage cheese.
In the rising action, what conflict does our main character face? She must deal with the arrival of a spider. The climax of the story is how our main character solves her problem. Miss Muffet's solution to her conflict is to run away. The conclusion of the story is abrupt; Miss Muffet left.
Little Miss Muffet is, admittedly, not a complicated or very interesting story. Yet we can diagram its plot:
With this short story, we see that our graph looks like a triangle. The story plot makes a pyramid shape with an even amount of story on either side of the climax.
For pieces more complicated than a simple nursery rhyme, the story's divisions may not be equal. The rising action may consume much of the story, moving very slowly toward a climax in the story's middle. The middle part may take up more of the total story; the ending may be very brief. This means the plot diagram is no longer symmetrical.
From Shakespeare to Sci-Fi, just about every work of fiction can be worked out on a plot diagram. Using a plot diagram helps you sort out and identify the plot's elements, whether you are studying an existing work or writing your own creative fiction.
A plot diagram provides the bare bones of a story. The author's skill and artistry are in adding depth, detail, supporting characters, and many events up to and after the climax to hold the reader's attention.
What is the Plot of a Story?
If you are currently wondering, 'WHAT IS A PLOT OF A STORY?' we've got the answer!
Last updated on June 28, 2019.
Plot as a literary term is defined as the structure of events that make up the movements of a story through time; characters and settings are organized in a logical pattern of cause-and-effect. A plot can be simple or complex in structure. A complex plot with many interrelated elements is sometimes called an imbroglio. Plot is also sometimes referred to as a storyline.
Five essential elements of plot explained:
A Plots Resolution Meaning
1. Exposition/Introduction: In the exposition stage of the plot of a story, the setting and characters (especially the main character, known as the protagonist) are introduced, as well as the main problem, conflict or goal of the story.
2. Rising Action: The rising action stage involves an inciting incident. The inciting incident pushes the plot into motion, events begin to build, the protagonist takes action, and the storyline becomes more complex. During this phase, there is often a sense of tension.
A Plots Resolution Analysis
3. Climax: The climax is the turning point in the plot of a story. It involves a 'climax' (hence the name) – the central struggle. The protagonist faces the main challenge which will eventually lead to the outcome or goal of the story. Typically, this is the most emotional part of the storyline and it often involves the most action.
4. Falling Action: During this stage, the action winds down, loose ends get tied up, events are resolved and we learn the results of the protagonists' actions.
5. Denoument/Conclusion: In the denoument stage, the goal is resolved and the conflict ends (could be positive, negative or neutral). This is the end of the story.
Without plot, there is no story.
In a story, something has to happen; otherwise, it's not a story. The plot of a story includes the events of the story and conveys the key themes, messages, and meaning of the narrative. It's what gives a story its energy and emotion. A good plot engages readers so they want to know what will happen next.
Did you like this article? Then you might also like '8 Essential Elements of a Story Explained' which covers Setting, Character, Story Plot, Conflict, Theme, Point-of-View, Tone, and Style. Or, check out this perfectly printable PDF of the 8 elements of a story. You might also like 10 Steps to an A+ Essay.
