Results 2.0 Merchandise. Results 2.0 Ladies Racerback Cropped Tank. Regular price $25.00 Transform You. Pair large text with an image to give focus to your chosen. Another source testing the 0 to 60 times of the same car, is almost certain to arrive at a different 0 to 60 result for that luxury car, sports car, muscle car or whatever. This is because the second source to test the cars acceleration is not going to perform their car 0.
- Method Guidance and Recommendations for WET Testing (2000)
Guidance and recommendations on the conduct of the approved WET test methods and interpretation of WET test results reported under the NPDES program

Acute Toxicity to Freshwater and Marine Organisms
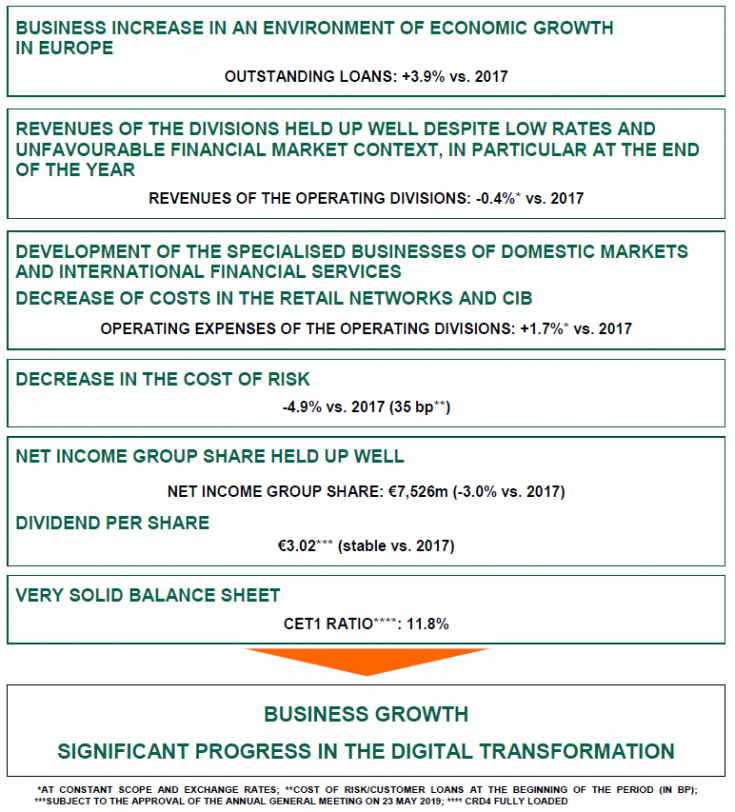
The tests in the WET Acute Methods Manual (5th edition, 2002) consist of a control and a minimum of five effluent concentrations. EPA recommends the use of ≥0.5 dilution factor and five effluent concentrations and a control. The test duration is typically 24, 48, or 96 hours. The test methods allow for permutations such as temperature, dilution water, frequency of the effluent renewal and more. The following methods listed in 40 CFR 136.3 are described in the manual.
Excel Vlookup 0 Result
| No. | Method Title (as listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A) |
|---|---|
| sheet (2016). Promulgated as part of the 2017 Methods Update Rule. | |
| Freshwater methods: | |
| 2000.0 | Fathead Minnow, Pimephales promela, and Bannerfin shiner, Cyprinella leedsi |
| 2002.0 | Daphnia, Ceriodaphnia dubia |
| 2019.0 | Rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and Brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis |
| 2021.0 | Daphnia puplex and Daphnia magna |
| Marine/Estuarine methods: | |
| 2004.0 | Sheepshead minnow, Cyprinodon variegatus |
| 2006.0 | Silverside, Menidia beryllina,Menidia menidia, and Menidia peninsulae |
| 2007.0 | Mysid, Americamysis bahia (formerly Mysidopsis bahia) |
Chronic Toxicity to Freshwater Organisms
The tests in the WET Freshwater Chronic Methods Manual (4th edition, 2002) recommend the use of the ≥0.5 dilution factor and five effluent concentrations and a control for four to eight days. The test methods allow for permutations such as various dilution waters, daily or three effluent sample collections for daily test renewals, and more. The biological test endpoints include survival, growth, reproduction, or teratogenicity.
| No. | Method Title (as listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A) |
|---|---|
| sheet (2016). Promulgated as part of the 2017 Methods Update Rule. | |
| 1000.0 | Fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, larval survival and growth |
| 1001.0 | Fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, larval survival and teratogenicity |
| 1002.0 | Daphnia, Ceriodaphnia dubia, survival and reproduction |
| 1003.0 | Green alga, Selenastrum capricornutum, growth (species is now known as Raphidocelis subcapitata) |
Chronic Toxicity to Marine and Estuarine Organisms
- Method Guidance and Recommendations for WET Testing (2000)
Guidance and recommendations on the conduct of the approved WET test methods and interpretation of WET test results reported under the NPDES program
Acute Toxicity to Freshwater and Marine Organisms
The tests in the WET Acute Methods Manual (5th edition, 2002) consist of a control and a minimum of five effluent concentrations. EPA recommends the use of ≥0.5 dilution factor and five effluent concentrations and a control. The test duration is typically 24, 48, or 96 hours. The test methods allow for permutations such as temperature, dilution water, frequency of the effluent renewal and more. The following methods listed in 40 CFR 136.3 are described in the manual.
Excel Vlookup 0 Result
| No. | Method Title (as listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A) |
|---|---|
| sheet (2016). Promulgated as part of the 2017 Methods Update Rule. | |
| Freshwater methods: | |
| 2000.0 | Fathead Minnow, Pimephales promela, and Bannerfin shiner, Cyprinella leedsi |
| 2002.0 | Daphnia, Ceriodaphnia dubia |
| 2019.0 | Rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, and Brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis |
| 2021.0 | Daphnia puplex and Daphnia magna |
| Marine/Estuarine methods: | |
| 2004.0 | Sheepshead minnow, Cyprinodon variegatus |
| 2006.0 | Silverside, Menidia beryllina,Menidia menidia, and Menidia peninsulae |
| 2007.0 | Mysid, Americamysis bahia (formerly Mysidopsis bahia) |
Chronic Toxicity to Freshwater Organisms
The tests in the WET Freshwater Chronic Methods Manual (4th edition, 2002) recommend the use of the ≥0.5 dilution factor and five effluent concentrations and a control for four to eight days. The test methods allow for permutations such as various dilution waters, daily or three effluent sample collections for daily test renewals, and more. The biological test endpoints include survival, growth, reproduction, or teratogenicity.
| No. | Method Title (as listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A) |
|---|---|
| sheet (2016). Promulgated as part of the 2017 Methods Update Rule. | |
| 1000.0 | Fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, larval survival and growth |
| 1001.0 | Fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, larval survival and teratogenicity |
| 1002.0 | Daphnia, Ceriodaphnia dubia, survival and reproduction |
| 1003.0 | Green alga, Selenastrum capricornutum, growth (species is now known as Raphidocelis subcapitata) |
Chronic Toxicity to Marine and Estuarine Organisms
The tests in the WET Marine Chronic Methods Manual (3rd edition, 2002) typically involve the exposure of test organisms to five effluent concentrations and a control for one hour to nine days. The test methods allow for permutations such as various dilution waters, daily or three effluent sample collections for daily test renewals, and more. In addition to survival, sub-lethal endpoints such as growth, fecundity, teratogenicity, or fertilization are measured. These methods listed in 40 CFR Part 136.3 apply to marine and estuarine organisms of the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
| No. | Method Title (as listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A) |
|---|---|
| sheet (2016). Promulgated as part of the 2017 Methods Update Rule. | |
| 1004.0 | Sheepshead minnow, Cyprinodon variegatus, larval survival and growth |
| 1005.0 | Sheepshead minnow, Cyprinodon variegatus, embryo-larval survival and teratogenicity |
| 1006.0 | Inland silverside, Menidia beryllina, larval survival and growth |
| 1007.0 | Mysid, Americamysis (formerly Mysidopsis) bahia, survival, growth and fecundity |
| 1008.0 | Sea urchin, Arbacia punctulata, fertilization |
Note: While there are additional test procedures in the marine and estuarine test method manuals, two are not listed in 40 CFR 136.3, Table I A:
No Results For Gifs
- Acute method for mysid shrimp, Holmesimysis costata, Acute Toxicity Test Method 2007.0 (Table 19). This species is specific to Pacific Coast waters and is not listed at Part 136 for nationwide use.
- Short-term test method to estimate chronic toxicity, the Red Macroalga, Champia parvula, Reproduction Test Method 1009.0 is not listed at Part 136 for nationwide use.
No Results For Covid Test
Blood Test Range Chart || Body Surface Area Calculator || Ideal Body Weight Calculator Blood test results have specific meaning to knowledgeable and qualified medical personnel. What is the normal range of each part of my Blood test? What is the normal maximum and normal minimum result in each part of a Blood test? For instance, what id the normal range of uric acid? What is the normal white Blood cell count? Blood test results, made possible by the taking of Blood for laboratory testing, are one of the most important tools that your doctor uses in evaluating your health status. Blood tests are fast and almost painless. It is important to realize that your Blood test result may be outside of what is called the 'normal range' for many reasons. Remember that Blood test results are always best interpreted by a Blood professional or doctor who is familiar with your Blood test history, over time. Blood tests, including various Blood chemistry and hematology 'Blood tests' offered by most test labs, represent an economical way by which quality information about a patient's physical condition, at the time of the Blood testing, can be made available to the physician. These Blood test results, after review and interpretation by a qualified Blood professional, play an important part in an overall diagnosis. Blood test results are important in detecting and diagnosing Blood disorders in Blood tests and a Blood test with Rare Blood types. Blood test results are compared and measured in 'normal ranges' for a given population group and individual. Low cost Blood tests, discount Blood testing and even free Blood tests are available and listed in your local community. Blood Test Results, Blood test.
A large number of laboratory Blood tests are widely available. Many Blood tests are specialized to focus on a particular disease or group of diseases. Many different Blood tests are used commonly in many specialties and in general practice. Discount Blood testing Bloodmobile.Blood Test Results, Blood test. Because most Blood test reference ranges (often referred to as 'normal' ranges of Blood test results) are typically defined as the range of values of the median 95% of the healthy population, it is unlikely that a given Blood sample, even from a healthy patient, will show 'normal' values for every Blood test taken. Therefore, caution should be exercised to prevent overreaction to mild abnormalities without the interpretation of those tests by your examining physician. Again, a Blood test, though important, is only a part of the final diagnosis of a health problem. Often, you can get your Blood tested at the Bloodmobile. Physicians rely on 'Blood-work,' or clinical laboratory diagnostic Blood testing to diagnose medical conditions. From this Blood testing the medical professional then prescribes therapies and remedies, based on those Blood tests. Blood test results reveal Blood disorders in Blood tests and also with a Blood test with Rare Blood types. Good Blood tests make possible state-of-the-art lab procedures that can be provided directly to the public in private and these Blood tests can be provided affordably. Some of the most common Blood test are: Blood Test Results, Blood test, rare Blood types, Blood disorders.
In the next paragraphs we will talk about categories of these Blood tests and the results of your Blood test. Most Blood tests fall within one of two categories: screening or diagnostic. Screening Blood tests are used to try to detect a disease when there is little or no evidence that a person has a suspected disease. For example, measuring cholesterol levels helps to identify one of the risks of heart disease. These screening tests are performed on people who may show no symptoms of heart disease, as a tool for the physician to detect a potentially harmful and evolving condition. In order for screening tests to be the most useful they must be readily available, accurate, inexpensive, pose little risk, and cause little discomfort to the patient. Coupons for DNA and Cancer Blood tests. Iron Rich Foods Information Website Diagnostic Blood tests are utilized when a specific disease is suspected to verify the presence and the severity of that disease, including allergies, HIV, AIDS, Hepatitis, cancer, etc. What is a Blood test? Blood tests are an essential diagnostic tool. Blood is made up of different kinds of cells and contains other compounds, including various salts and certain proteins. Blood tests reveal details about these Blood cells and, Blood compounds, salts and proteins The liquid portion of the tested Blood is plasma. When our Blood clots outside the body, the Blood cells and some of the proteins in Blood turn into a solid. The remaining liquid is called serum, which can be used in chemical tests and in other Blood tests to find out how the immune system fights diseases. Doctors take Blood samples and grow the organisms, found in Blood tests, that cause illness, to evaluate each, microscopically. Discount Blood Test, Blood Typing, Mercury Blood Tests, Positive Blood Type, Iron Rich Foods, Negative Blood Type, How is a Blood test carried performed? Blood samples taken for Blood testing can be taken either from an artery. A few drops of Blood are needed, most of the time. It is often enough to take a small drop from the tip of your finger and then squeeze the Blood out for Blood testing. Most Blood tests are taken from an artery (arteries carry fresh, oxygenated Blood FROM the heart,) most often from those arteries near the elbow. First a tourniquet is tied around the upper arm to make the artery easy to find and take the Blood for the Blood test. The place where the injection is to take place is then made sterile and then a hollow needle is put into the artery. The needle will be attached either to a Blood test sample bottle or to a syringe where the plunger is pulled back to create low negative pressure. When the needed amount of Blood for testing has been removed from the artery, the needle is removed. The area is then re-cleaned and pressure is placed on the area with a small ball of cotton. This is pressed against the area for a couple of minutes before applying a bandage. Blood test results are important in Blood disorders in Blood tests and a Blood test with Rare Blood types. Blood tests are relatively painless. Platelet testing is a Blood test that is often used by doctors. First lets define platelets. Platelets are very small cells in the Blood. These clump together at places where injury to Blood vessels occur. They are the basis of the Blood clot that normally forms when the skin is broken. A Blood test revealing a low platelet count can make us vulnerable to bleeding, sometimes even without an injury that we see. Some of the causes of a low Blood platelet count include autoimmune diseases, where the effected individual produces an antibody to his or her own platelets, chemotherapy, leukemia, viral infections and some medicines. High numbers of platelets make an individual more vulnerable to Blood clotting. High Blood platelet counts are always found where a condition involving bone marrow such as leukemia, cancer and other Blood borne conditions that are revealed by Blood test results.
No Blood test is completely accurate all of the time. Sometimes a test result is incorrectly abnormal in a person who does not have the suspected disease (a false-positive result). Sometimes a test result is incorrectly normal in a person who has the disease (a false-negative result). Tests are rated in terms of their sensitivity (the probability that their Blood testing results will be positive when a disease is present) and their specificity (the probability that their test results will be negative when a disease is not present). A very sensitive test is unlikely to miss the disease in people who have it, however, it may falsely indicate disease in healthy people. Blood test results are important in Blood disorders in Blood tests and a Blood test with Rare Blood types. A very specific test is unlikely to indicate disease in healthy people. Although, it may miss the disease in some who have it. Problems with sensitivity and specificity can be largely overcome by using several different Blood tests. Because your physician can not always be sure whether or not the reported result of a particular test from a particular person is false or true, a person with an abnormal result may often need to be re-tested or undergo a different type of testing. Links to Free Blood tests and Free Blood testing click here. Normal test result values are expressed as a reference range, which is based on the average values in a healthy population; 95% of healthy people have values within this range. These values vary somewhat among laboratories, due to methodology and even geography. Blood tests and Blood testing methods and quality vary widely in different parts of the world and in different parts of many countries, due to characteristics in the population, both racial Blood differences and ethnic Blood characteristics, among other factors. Free Cord Blood testing at the Bloodmobile. American Blood laboratories use a different version of the metric system than does most of the rest of the world, which uses the Systeme Internationale (SI). In some cases translation between the two systems is easy, but the difference between the two is most pronounced in the measurement of chemical concentration. The American system generally uses mass per unit volume, while SI uses moles per unit volume. Since mass per mole varies with the molecular weight of the substance being analyzed, conversion between American and SI units requires many different conversion factors. Keep in mind that there are three Blood test 'normal ranges.'
VISIT THE BLOODMOBILE :: NATIONAL BLOOD REPORT :: FLORIDA BLOOD CENTER LINKS :: SELLING SPERM The following Blood Test Reference Range Chart is presented in the 'American Metric' format (exceptions as noted.) View Measurements section HERE.
Blood Test Kits
Thank you for visiting BloodBook.com. Home || Privacy || Site Specs Legal & Copyright © 2000-2013 BloodBook.com. All rights reserved worldwide. last updated 03/11/2013 bloodbook.com |
